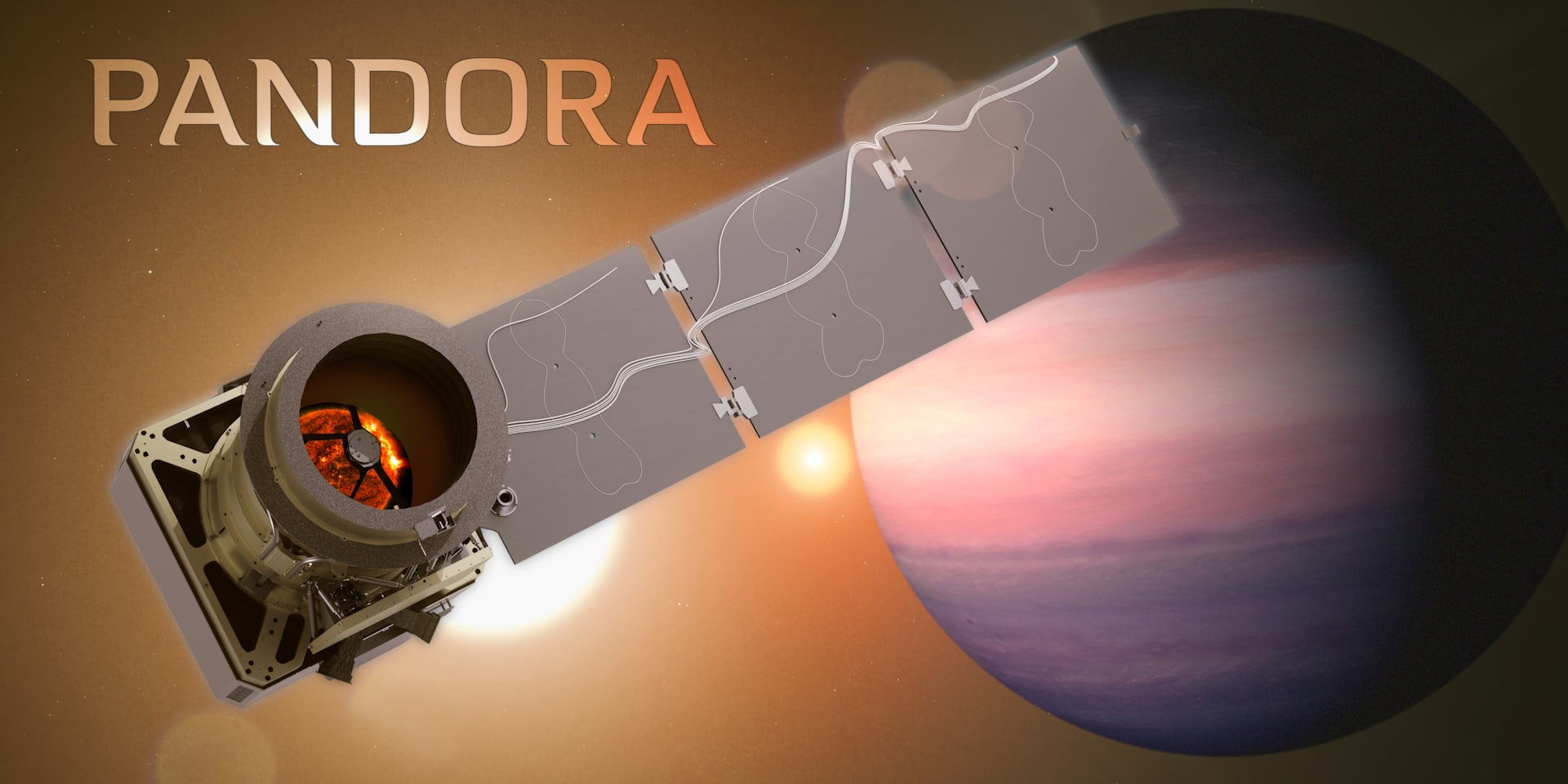
The search for life beyond Earth has long been a fascinating topic in the scientific community. With the launch of the Pandora telescope, NASA has taken a significant step forward in this quest. This new telescope is designed to detect biosignatures, or signs of life, in the atmospheres of exoplanets.
Key Features and Capabilities of the Pandora Telescope
The Pandora telescope is a highly advanced instrument designed to study the atmospheres of exoplanets in unprecedented detail. It features a state-of-the-art spectrograph that can detect subtle changes in the light passing through the atmospheres of distant worlds.
This allows scientists to identify potential biosignatures, such as the presence of oxygen, methane, or other gases that could be indicative of life.
Building Upon the Success of the James Webb Space Telescope
The Pandora telescope is not a replacement for the James Webb Space Telescope, but rather a complementary instrument that will work in conjunction with JWST to search for habitable worlds.
JWST has already made significant contributions to our understanding of the universe, including the detection of water vapor on a distant exoplanet. The Pandora telescope will build upon this success, providing a more detailed understanding of the atmospheres of these distant worlds.
Future Research and Discoveries
The Pandora telescope will be used to study a wide range of exoplanets, from rocky worlds to gas giants. By analyzing the atmospheres of these planets, scientists hope to gain a better understanding of the conditions necessary for life to exist.
Future research will also focus on identifying potential targets for future missions, such as the detection of biosignatures in the atmospheres of exoplanets.
The Pandora telescope is a major milestone in the search for extraterrestrial life. With its advanced capabilities and state-of-the-art technology, this instrument has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe and our place within it.